What is OCR?
OCR is a technology that allows machines to read printed text and images. It is often used in business applications, such as digitizing documents for storage or processing, and in consumer applications, such as scanning a receipt for expense reimbursement.
OCR stands for Optical Character Recognition. The term “character” refers to both letters and numbers. OCR software can recognize whether a given image contains characters or not and then identify the characters within it.

OCR Scope
The global optical character recognition market is expected to grow rapidly in the coming years. The market size of OCR was valued at USD 8.93 billion in 2021. It is expected to grow at a CAGR of 15.4% between 2022 and 2030. This growth is driven by the increasing demand for OCR in various end-use industries, such as healthcare, automotive, and others.
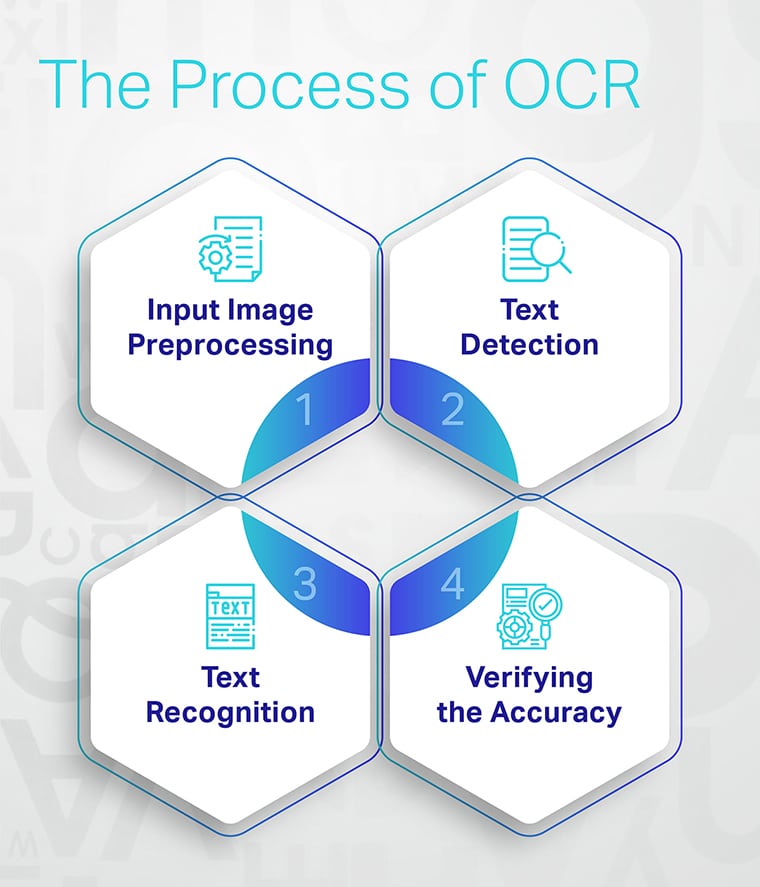
The Process of OCR
Optical Character Recognition is a detailed process that helps extract text from images using NLP.
- The first step in OCR is to process the input image. This involves cleaning up the image and making it suitable for further processing.
- Next, the OCR engine searches for regions that contain text in the image. The engine segments these regions into individual characters or words so they can later be identified during text recognition.
- Using the results from text detection, the OCR engine identifies each character by its shape and size. You’ll often see convolutional and recurrent neural networks, sometimes in combination, being used for this task.
- Once OCR software has finished recognizing text in an image file, it must be verified as accurate before it can be used.
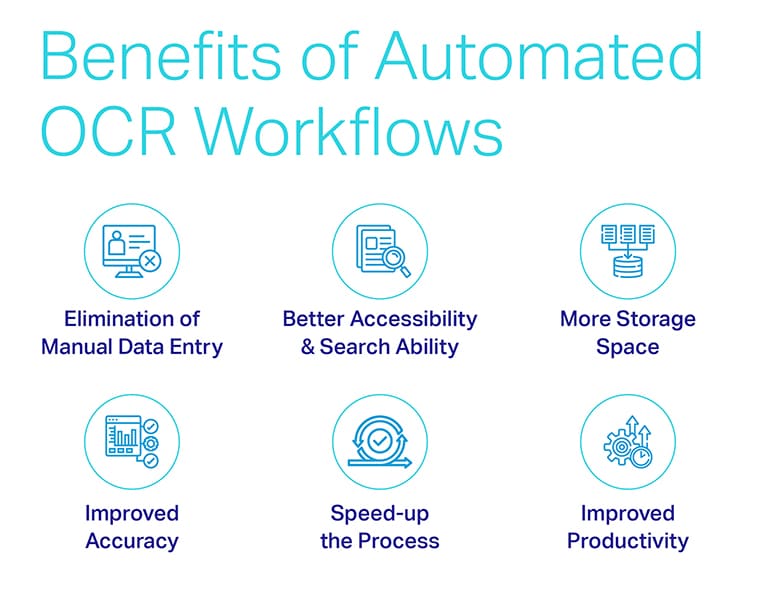
Benefits of Automated OCR Workflows
Key benefits of Automated Optical Character Recognition Workflows include:
- Faster, more accurate, automated results while eliminating human error.
- Lower cost of entry for small businesses due to faster data processing and efficient data utilization.
- More consistent results across multiple users and projects.
- Improved data storage and data security.
- Huge scope for scalability.

OCR Challenges
The main issue with OCR is that it isn’t perfect. If you imagine reading the text on this page through a camera and then converting those images into words, you’ll get an idea of why OCR can be problematic. Some of the challenges for OCR include:
- Blurry text distorted by shadows.
- The color of the background and the text have similar colors.
- Parts of the image are cut off or cropped out entirely (such as the bottom portion of “this”).
- Faint marks on top of some letters (such as “i”) may confuse OCR software into thinking they’re part of the letter rather than marks on top.
- Different font types and sizes may be difficult to identify.
- The lighting conditions when taking the picture or scanning the document.

OCR Use Cases
- Data entry automation: OCR can be used to automate the process of entering data into a database.
- Barcode scanning: OCR allows a computer to scan bar codes on products and retrieve information about them from databases.
- Number plate recognition: OCR analyzes license plates and extracts information such as registration numbers and state names from them.
- Passport verification: OCR can be used to verify the authenticity of passports, visas, and other travel documents.
- Recognizing store labels: Stores can use OCR to automatically read their product labels and compare them with their product catalogs to determine what products are currently on store shelves, out-of-stock items, or stockroom errors.
- Insurance claims processing: OCR software can scan paperwork and verify signatures, dates, addresses, and other information on forms submitted by customers who have filed claims for damage done by natural disasters, fires, or theft.
- Reading traffic lights: An OCR system can be used to read the colors on traffic lights and determine whether they are red or green.
- Reading utility meters: Utility companies use OCR to read electric, gas, and water meters to bill customers for the correct amounts.
- Social media monitoring – Companies use OCR to identify and classify mentions of a company or brand in social media posts, tweets, and even Facebook updates
- Verifying legal documents: A law office may scan documents such as contracts, leases, and agreements to ensure they’re legible and accurate before sending them out to clients.
- Multilingual documents: A company that sells products in other countries may need to translate its marketing materials into multiple languages and then OCR them to be used as templates for future projects.
- Medical drug labels: OCR is used extensively to extract meaningful information from drug labels so that computer systems can analyze and process them.

Industry
- Retail: The retail industry uses OCR to scan barcodes, credit card information, receipts, etc.
- BSFI: Banks use OCR to read checks, deposit slips, and bank statements to verify signatures and add transactions to accounts. They can also analyze large amounts of data to make decisions about customer accounts, investments, loans, and more with OCR.
- Government: OCR can be used to scan and digitize legal documents, such as birth certificates, driver’s licenses, and other official records.
- Education: Teachers can use OCR to create digital copies of books and other student documents. Teachers can also scan documents into their computers and use OCR technology to create an electronic copy that students can access anytime.
- Healthcare: Doctors often need to enter patient information into a computer system quickly. The healthcare industry can use OCR for business processes such as billing and claims processing.
- Manufacturing – Manufacturing plants often need to scan documents such as invoices or purchase orders. OCR can be used to “read” the serial numbers on product components as they pass by on a conveyor belt or through an assembly line.
- Technology: OCR software is used in many settings related to IT, including data mining, image analysis, speech recognition, and more. In software development, OCR is used to convert scanned documents back into digital files.
- Transport and logistics: OCR can be used to read shipping labels or monitor warehouse inventory. It can also detect fraud when vendors submit invoices for payment.
Verdict
The OCR process is relatively simple, requiring only a few steps to transform an image into text. There are some errors and inconsistencies, but the technology is undeniably impressive, given how it all works.